Cameras
How CCTV Cameras Work – A Complete Guide to Modern Surveillance Systems
In today’s world, surveillance is no longer a luxury — it’s a necessity. Whether you want to secure your home, business, or public space, Closed-Circuit Television (CCTV) cameras are among the most reliable tools available for safety and monitoring. Understanding how CCTV cameras work helps you choose the right system, optimize coverage, and make the most of your investment in security.
What Is a CCTV System and Why Is It Used?
A CCTV system is a network of cameras designed to capture, transmit, and record video footage within a closed circuit. Unlike broadcast television, the footage is not shared publicly — it is sent to designated monitors or recorders for real-time viewing or playback.
The main purpose of CCTV systems is to deter criminal activity, monitor activities, and collect evidence when needed. They are used in homes, offices, retail stores, construction sites, and even across entire cities as part of smart security networks.
Studies across the security industry have shown that visible surveillance can reduce burglary and vandalism attempts by more than 50%, making CCTV one of the most effective preventive tools for safety.
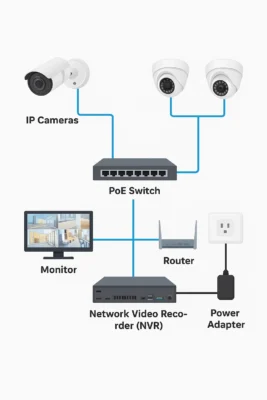
Key Components of a CCTV Camera System
A reliable CCTV setup includes several interconnected parts. Each plays a specific role in ensuring smooth, uninterrupted monitoring.
-
Cameras
Cameras are the foundation of every system. They capture the footage and send it for processing.
Common types include:
- Analog cameras: Use coaxial cables to send video signals to a DVR.
- IP cameras: Send digital footage over a network to an NVR.
- Dome cameras: Ideal for indoor use; discreet and wide-angled.
- Bullet cameras: Designed for outdoor monitoring; weather-resistant and long-range.
- PTZ cameras (Pan-Tilt-Zoom): Allow rotation and zoom control to monitor larger areas.
Brands like Hikvision and CP Plus offer advanced options featuring high-definition recording, infrared night vision, and motion detection.
-
Lens and Image Sensor
The lens controls how much of the area the camera sees, while the sensor (CCD or CMOS) converts light into electronic signals. High-resolution sensors capture sharper, more detailed images even in low light conditions.
-
Recorder (DVR/NVR)
- DVR (Digital Video Recorder): Used with analog systems. It receives raw signals from cameras and converts them into digital video files.
- NVR (Network Video Recorder): Used with IP and wireless systems. It records digital footage transmitted over Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
-
Monitor and Video Management Software
A monitor displays live or recorded video feeds, while VMS (Video Management Software) helps control multiple cameras, replay footage, and set motion alerts from one dashboard.
-
Power and Connectivity
Cameras need a power source — either via:
- Traditional electrical supply
- Power over Ethernet (PoE), where both power and data travel through one cable
- Rechargeable batteries in some wireless models
-
Storage Options
Footage can be stored on:
- Hard drives inside DVRs or NVRs
- Network storage (NAS) for larger systems
- Cloud storage, which allows remote access and longer retention
Step-by-Step – How a CCTV Camera System Works
Let’s break down the process of how CCTV systems capture and deliver live video:
- Image Capture:
The camera lens captures visual data through its sensor. - Signal Transmission:
- Analog systems send video through coaxial cables to a DVR.
- IP and wireless systems send digital data through Ethernet or Wi-Fi to an NVR or the cloud.
- Recording and Compression:
Footage is encoded using formats like H.264 or H.265, which reduce file size without losing quality. - Monitoring and Playback:
You can view the live feed on monitors, smartphones, or web portals. - Remote Access (Real-Time CCTV Live):
Many modern systems offer mobile apps for live streaming, playback, and alerts — giving users access from anywhere, at any time.
Wired vs. Wireless CCTV Cameras – What’s the Difference?
Wired CCTV Systems
- Depend on cables for power and data.
- Deliver stable and uninterrupted connections.
- Best suited for large buildings, offices, and multi-camera setups.
Wireless CCTV Systems
Wireless systems transmit footage via Wi-Fi. They are quick to install and ideal for smaller spaces or rental properties.
Wi-Fi CCTV cameras connect directly to routers and can upload footage to an NVR or cloud server.
However, they rely on strong internet signals and still require a power source.
Wireless systems are increasingly popular in homes because they offer flexibility, mobile access, and easy scalability.
Where and Why CCTV Cameras Are Used
CCTV systems serve different purposes across sectors:
- Residential Security: Protects homes, driveways, and entry points. Users can access live video through mobile apps.
- Commercial Buildings: Helps reduce theft, monitor employees, and manage workplace safety.
- Industrial and Construction Sites: Monitors equipment, materials, and worker safety in real time.
- Public Areas: Used by authorities for traffic management, crowd control, and emergency monitoring.
- Smart Cities: Integrated with AI analytics for identifying incidents and improving urban safety.
Benefits of CCTV Systems for Modern Security
- Crime Deterrence: Cameras discourage trespassers and intruders.
- Evidence Collection: Recorded footage helps in investigations and insurance claims.
- Remote Monitoring: Access your system anywhere, anytime via mobile or web apps.
- Workplace Safety: Ensures compliance and prevents accidents.
- Operational Insight: Businesses use CCTV to monitor operations and productivity.
How Long Does CCTV Footage Stay Stored?
The duration depends on storage capacity and video quality:
- Basic systems: 7–15 days
- Business installations: 30–90 days
- Cloud systems: Several months or more
To maximize storage, use efficient compression formats and schedule automatic backups. Systems with 4TB or higher storage can record HD video continuously for weeks.
Maintenance Tips to Keep Your CCTV Running Smoothly
- Clean lenses regularly to remove dust or smudges.
- Check connections and power supply monthly.
- Update firmware for better security and performance.
- Test remote access and alerts periodically.
- Back up recordings on external or cloud drives.
Regular maintenance ensures your system stays reliable for years.
Future of CCTV – AI and Smart Surveillance
The next generation of CCTV cameras is powered by Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things (IoT) technology.
Modern systems can:
- Detect unusual motion or behavior automatically.
- Recognize faces and vehicle license plates.
- Send instant alerts to mobile devices.
- Integrate with smart lights, alarms, and access control systems.
AI-powered analytics are turning CCTV from a passive security tool into a proactive monitoring solution, making it a vital part of smart homes and smart cities.
Conclusion
CCTV cameras play an essential role in today’s security-driven world. From small apartments to commercial towers, these systems provide constant visibility and peace of mind. Knowing how CCTV works helps you select the right system — whether wired, wireless, or AI-enabled — for your exact needs.
If you’re planning to install or upgrade your CCTV setup, choose quality products and CCTV installation support to ensure maximum safety and performance.
FAQs About CCTV Systems
Yes. Wired systems can record locally to DVRs or NVRs even without internet. Connectivity is only needed for remote access.
They pair with your router through encrypted wireless signals, transmitting video to a connected NVR or cloud storage.
Most standard cameras cover 20–40 meters. High-end PTZ models can monitor up to 200 meters or more.
DVRs are for analog systems, while NVRs record video from digital IP cameras through a network.
Yes, as long as cameras do not record private areas like neighbors’ properties or bathrooms.