Uncategorized
Difference Between Router and Switch: A Complete Networking Guide for Beginners
Although routers and switches are often used together, they serve very different purposes and operate at different layers of the network model. Many beginners and even business users get confused between the two, assuming they perform the same function. In reality, understanding the difference between a router and a switch is critical for designing an efficient network.
This guide explains what a router is, what a switch is, how they work, their types, advantages, and key differences, in a simple and easy-to-understand manner.
What Is a Router?
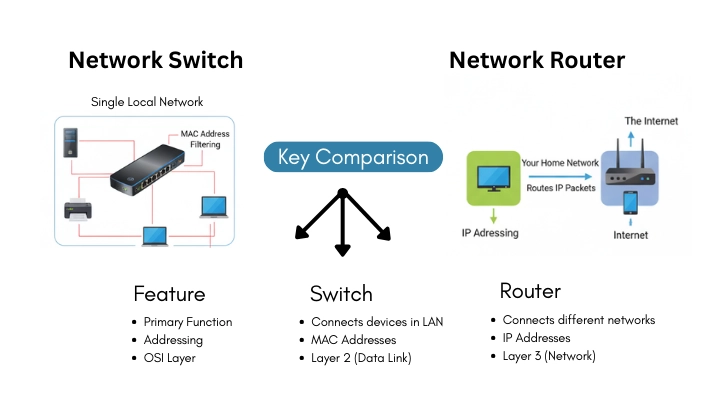
A router is a networking device that connects multiple networks and directs data traffic between them. It operates at the Network Layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model and is responsible for determining the best possible path for data packets to reach their destination.
Routers are commonly used to connect local networks (LANs) to the internet (WAN). They make intelligent decisions based on IP addresses and routing tables to ensure data reaches the correct destination efficiently.
How a Router Works
A router performs several important tasks within a network:
- It connects different networks such as a local office network and the internet.
- It assigns local IP addresses to devices using DHCP.
- It receives data packets and examines their destination IP address.
- It selects the fastest and most efficient path using routing algorithms.
- It forwards data packets to the correct next hop until they reach the destination.
Because of this intelligent routing capability, routers prevent unnecessary traffic congestion and ensure reliable data delivery.
Types of Routers
1. Wireless Router
Wireless routers are the most commonly used routers in homes and offices.
Key features:
- Provide Wi-Fi connectivity without physical cables
- Support multiple devices simultaneously
- Use security features like WPA2/WPA3 encryption
- Ideal for laptops, smartphones, and smart devices
Wireless routers are easy to install and offer flexibility, making them suitable for modern workplaces.
2. Wired Router
Wired routers require Ethernet cables to connect devices.
Key features:
- More stable and consistent connection
- Higher security compared to wireless
- Often used in schools, data centers, and small businesses
- Can support VoIP and additional network services
Many wired routers also include built-in wireless access points.
Advantages of Using a Router
- Connects multiple networks securely
- Provides internet access to many devices
- Reduces network congestion using intelligent routing
- Supports firewall and security policies
- Offers NAT (Network Address Translation) for IP management
- Enables controlled and protected data flow
What Is a Network Switch?
A network switch is a core networking device used to connect multiple devices within the same local area network (LAN) and allow them to communicate efficiently. It operates at the Data Link Layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model and forwards data using MAC (Media Access Control) addresses.
Unlike a router, a switch does not connect different networks. Instead, it focuses on improving internal data transmission, ensuring faster speeds, reduced congestion, and better overall network performance within an organization or home network.
How Does a Switch Work?
Every device connected to a switch has a unique MAC address. The switch automatically learns these addresses and stores them in a MAC address table, allowing it to make intelligent forwarding decisions.
The switching process includes:
- Receiving data frames from a connected device
- Identifying the destination MAC address
- Sending data only to the correct port
- Avoiding unnecessary network-wide broadcasts
- Minimizing collisions and optimizing data flow
Because data is forwarded only where it is needed, switches are significantly faster and more efficient than hubs, making them ideal for modern networks.
Types of Network Switches
1. Managed Switch
Managed switches provide advanced configuration, monitoring, and control capabilities, making them suitable for professional and enterprise environments.
Key benefits include:
- VLAN configuration for network segmentation
- Real-time traffic monitoring and bandwidth control
- Enhanced security and access management
- Improved performance optimization
- Ideal for business, enterprise, and data center networks
2. Unmanaged Switch
Unmanaged switches are simple plug-and-play devices that require no technical configuration.
Key benefits include:
- Easy installation with no setup required
- Budget-friendly networking solution
- Suitable for homes, small offices, and basic networks
- Limited control, monitoring, and security features
Advantages of Using a Network Switch
- Enhances internal network performance
- Reduces data collisions and network congestion
- Increases overall available bandwidth
- Enables direct and efficient device-to-device communication
- Improves network reliability and stability
- Supports full-duplex communication for faster data transfer
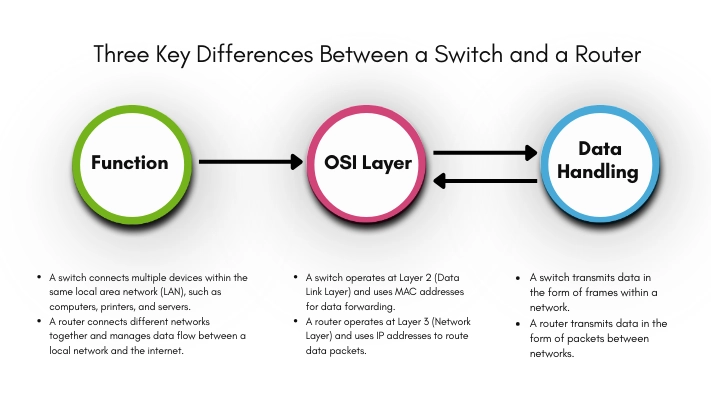
Key Differences Between Router and Switch
| Feature | Router | Switch |
| Main Function | Connects multiple networks | Connects devices within a network |
| OSI Layer | Network Layer (Layer 3) | Data Link Layer (Layer 2) |
| Data Type | Data packets | Data frames |
| Address Used | IP Address | MAC Address |
| NAT Support | Yes | No |
| Network Scope | LAN, MAN, WAN | LAN only |
| Cost | Generally, more expensive | Cheaper than routers |
| Security | Advanced security & firewall | Basic security |
| Traffic Control | Intelligent routing | Efficient forwarding |
Router vs Switch: Which One Do You Need?
- Use a router if you need internet access or want to connect multiple networks.
- Use a switch if you want to connect multiple devices within the same local network.
- In most business environments, routers and switches are used together to create a complete network infrastructure.
Conclusion
Routers and switches are both essential networking devices, but they serve different and complementary purposes. A router acts as the gateway between networks, while a switch ensures fast and efficient communication within a network.
Understanding the difference between a router and a switch helps businesses, IT administrators, and beginners design secure, scalable, and high-performance networks. Choosing the right combination of these devices ensures better connectivity, improved security, and long-term network reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A network switch is used to connect multiple devices within the same local area network (LAN) and allow them to communicate efficiently. It helps improve network speed, reduce data collisions, and manage internal traffic.
A switch connects devices within the same network using MAC addresses, while a router connects different networks using IP addresses. Switches improve internal communication, whereas routers manage data flow between networks and the internet.
A standard network switch operates at the Data Link Layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model. Some advanced switches, known as Layer 3 switches, can also perform limited routing functions.
A switch reduces congestion by sending data only to the specific device that needs it instead of broadcasting data to all devices. This targeted forwarding minimizes unnecessary traffic and improves performance.
Managed switches offer advanced features such as VLANs, traffic monitoring, and security controls, making them suitable for business networks. Unmanaged switches are plug-and-play devices designed for simple networks with minimal control requirements.