Uncategorized
Complete Guide to HDD vs SSD vs NVMe: How Each Storage Type Works
Your storage drive plays a major role in how your computer performs every day. From booting your operating system to loading applications, opening games, and processing heavy workloads—everything depends on whether your device uses an HDD vs SSD vs NVMe drive. In 2025, the performance gap between these technologies is wider than ever, making the right choice essential for gamers, professionals, content creators, and home users.
This guide explains all three storage types in detail, with real-world comparisons and practical recommendations. If you’re in the UAE, you can explore HDDs, SSDs, and NVMe drives at the best prices at Cost to Cost Trading UAE.
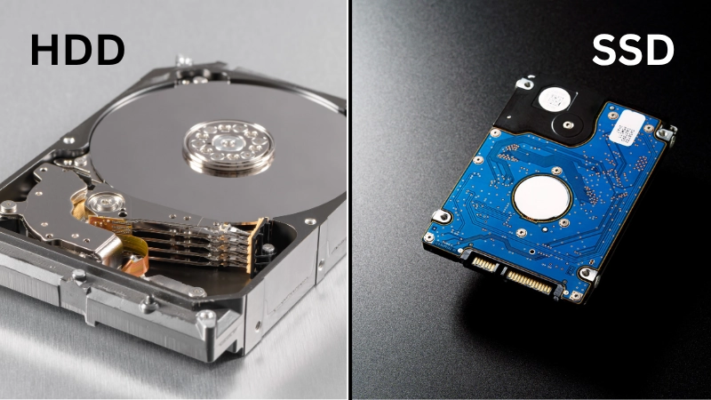
What is an HDD? (Hard Disk Drive)
An HDD is the oldest and most affordable storage technology still in use today. It stores data on spinning magnetic platters, and a mechanical arm moves across the disk to read and write information. Because this process depends on physical movement, Hard Drives UAE are slower and more prone to failure compared to modern solid-state storage. However, their large capacity and low cost keep them popular for storage-heavy tasks.
How HDDs Work
Inside an HDD, the platters spin at 5400 or 7200 RPM while the read/write arm positions itself over specific sectors on the disk. The magnetic surface stores data in patterns. This mechanical nature creates delays, causing high latency and slow performance. Even simple tasks like opening apps or booting Windows take much longer compared to SSDs or NVMe drives.
Benefits of HDDs
HDDs still offer unmatched cost-per-GB, making them excellent for bulk storage. Large drives—10TB, 12TB, even 20TB—are much cheaper than SSDs of the same size. They are commonly used for long-term backups, surveillance systems, media libraries, and servers that need massive storage but not high speed.
Best Uses
HDDs are best suited for non-performance tasks like storing movies, photos, documents, CCTV footage, and server backups. For operating systems or applications, HDDs are no longer recommended in 2025.
Pros and Cons – HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
Pros
- Cheapest cost per GB
- Large storage capacities (up to 20TB+)
- Great for backups & long-term archiving
- Mature, widely available technology
Cons
- Slowest read/write speeds
- High latency
- Can fail due to mechanical parts
- Noisy and generates more heat
- Not suitable for OS or gaming in 2025
What is an SSD? (Solid-State Drive)
SSDs are the modern standard for fast and reliable storage. Instead of mechanical parts, SSDs store data in NAND flash memory, allowing near-instant access. This results in much faster boot times, quicker file transfers, and smoother overall computing.
How SSDs Work
Unlike HDDs, SSDs store data in interconnected flash memory cells managed by a controller. Since there are no physical moving parts, the drive can instantly access any area, dramatically improve speed and reducing the risk of mechanical failure. SSDs use the SATA interface, which limits maximum speeds to around 550 MB/s—but still far faster than HDDs.
Benefits of SSDs
SSDs deliver silent operation, lower power consumption, minimal heat generation, and strong durability. They improve everything: the OS boots faster, games load quicker, and applications open almost instantly. Even older PCs feel brand new when upgraded with an SSD.
Best Uses
SATA SSDs are perfect for everyday computing, office work, budget gaming, content creation, and business applications. They offer great performance at an affordable price.
Pros and Cons –SSD (Solid-State Drive – SATA)
Pros
- 5–6× faster than HDD
- Silent operation
- Durable with no moving parts
- Affordable mid-range option
- Great improvement for old PCs
Cons
- More expensive per GB than HDD
- SATA interface limits speed (max ~550 MB/s)
- Lifespan depends on write cycles
- Not as fast as NVMe for heavy workloads
What is NVMe? (Non-Volatile Memory Express)
NVMe is the fastest and most advanced storage technology available today. It uses PCIe lanes—the same high-speed channels used by graphics cards—to communicate directly with the CPU. This eliminates bottlenecks and delivers extremely high speeds and ultra-low latency.
How NVMe Works
NVMe drives use multiple parallel data lanes, enabling thousands of simultaneous operations. This architecture allows NVMe drives to reach speeds of 3,000 MB/s to 7,000+ MB/s, far exceeding SATA SSD limits. Their latency is extremely low, making them perfect for heavy workloads like AI, professional editing, and gaming.
Benefits of NVMe
NVMe is built for performance. It dramatically improves loading times, boosts productivity, and accelerates data-intensive tasks. Large video files, AI datasets, and 3D models load in seconds instead of minutes. For gamers, textures stream instantly and stuttering is reduced.
Best Uses
NVMe is ideal for professionals, creators, developers, gamers, and anyone who needs the highest possible performance. It’s also perfect for boot drives in PCs and servers.
Pros and Cons – NVMe SSD (PCIe)
Pros
- Fastest storage technology available
- Extremely low latency
- Best for gaming, editing, AI, servers
- Speeds up to 7000 MB/s
- Perfect for high-end PCs and workstations
Cons
- Higher cost than SATA SSD
- Requires NVMe-compatible slot
- High-end NVMe (Gen4/Gen5) can heat up
- Overkill for basic users
Why Storage Technology Matters in 2025
Computers today demand more speed than ever before. Games come with massive high-resolution assets, AI models use huge training datasets, and video creators work with 4K–8K footage. Even everyday tasks like browsing the web or running Windows 11 benefit from fast storage.
If your storage is slow, your entire system feels slow—no matter how powerful your CPU or RAM is. In 2025, choosing the right drive is more important than ever.
Performance Comparison — HDD vs SSD vs NVMe (2025 Real Speeds)
The speed difference between HDD, SSD, and NVMe is massive. While HDDs struggle with basic tasks, SSDs offer a big improvement—and NVMe reaches extreme performance levels.
Real-World Speeds
|
Drive Type |
Typical Speed | High-End Speed |
|
HDD |
80–160 MB/s | ~200 MB/s |
| SATA SSD | 500–550 MB/s |
~600 MB/s |
| NVMe SSD | 3,000 MB/s |
7,000+ MB/s |
What This Means in Daily Use
- NVMe boots Windows in 4–6 seconds
- SATA SSD boots in 10–15 seconds
- HDD takes 40–60 seconds
- Games and apps launch instantly on NVMe
- Heavy software loads 5–10× faster
- Video editing renders faster
- AI dataset loading becomes smoother
NVMe offers a level of speed that dramatically changes the user experience.
How Each Drive Works — Detailed Explanation
How HDDs Work
HDDs rely on mechanical rotation and movement. This technology, although reliable for storage, is inherently slow and not suitable for modern performance needs. Heavy multitasking causes lag because the read/write head can only handle one operation at a time.
How SATA SSDs Work
SATA SSDs remove mechanical components, allowing much faster access times. However, their speed is limited by the SATA interface, which caps transfer rates to around 550 MB/s. For many users, this is more than enough.
How NVMe Works
NVMe bypasses SATA and connects directly to PCIe lanes. This is why NVMe SSDs outperform SATA SSDs by 5–10×. With PCIe 4.0 and PCIe 5.0 technology, speeds continue to rise each year.
NVMe vs SATA SSD — In-Depth Comparison
While both SSD and NVMe use flash memory, the interface sets them apart. SATA SSDs are great for upgrading old systems, but NVMe delivers true high-end performance.
|
Feature |
SATA SSD |
NVMe SSD |
|
Interface |
SATA III | PCIe 4.0 / 5.0 |
| Max Speed | ~550 MB/s |
3000–7000+ MB/s |
|
Latency |
0.1 ms |
<0.05 ms |
|
Best For |
General use |
High-end tasks |
| Cost | Lower |
Higher |
NVMe is the clear winner for speed, multitasking, and professional workloads.
Latency Comparison (Why NVMe Feels Instant)
Latency measures how fast a drive responds. NVMe’s extremely low latency makes every task faster and smoother.
|
Drive Type |
Latency |
| HDD |
5–10 ms |
|
SATA SSD |
0.1–0.2 ms |
| NVMe |
<0.05 ms |
IOPS Comparison (Multitasking Power)
IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) determines how many operations a drive can handle at once.
|
Drive Type |
IOPS |
| HDD |
~200 |
| SATA SSD |
~100,000 |
| NVMe |
500,000+ |
Higher IOPS = faster apps, smoother gaming, and quicker rendering.
Which Drive Should You Use? (Workload-Based Recommendations)
Gaming
Modern games load much faster on SSDs, but NVMe offers the best texture streaming and world loading.
AI & Machine Learning
AI workloads depend heavily on dataset access. NVMe drastically improves training pipelines.
Video Editing
For 4K/6K/8K footage, NVMe ensures faster decoding, scrubbing, and timeline playback.
Office Work
SATA SSDs provide plenty of speed for browsing, Excel, Word, and Teams.
Servers
For workload servers:
- NVMe = boot & software
- HDD = backups and large storage
Which Drive Should You Buy in 2025?
- Best Performance: NVMe SSD
- Best Value: SATA SSD
- Best for Storage: HDD
- Best Overall Setup: NVMe (OS) + HDD (Storage)
Where to Buy SSD, HDD & NVMe in UAE
Looking for genuine storage devices in Dubai, Sharjah, or Abu Dhabi?
Cost to Cost Trading offers:
- 100% Genuine HDD, SSD & NVMe
- Best prices in UAE
- Fast delivery
- Top brands available